Curriculum
Stoichiometric Relationship
INTRODUCTION TO THE PARTICULAR NATURE OF MATTER AND CHEMICAL CHANGE
0/2ASSIGNMENTS
0/2MOLE CONCEPT
0/2ASSIGNMENTS
0/2REACTING MASSES AND VOLUMES
0/2ASSIGNMENTS
0/2Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
Elements and Compounds
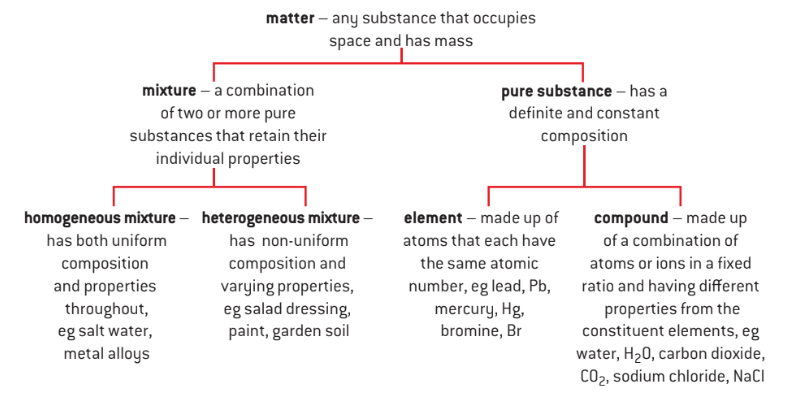
Chemistry is the study of different types of materials and their properties. We notice diverse chemical substances and elements all around us. It is consequently critical to classify and categorize them in order to study, analyse, and comprehend their qualities. Elements, compounds, and mixtures are the three types of matter. Elements and compounds are pure chemical substances found in nature. Whereas mixtures are impure substances in our environment. We will learn more about elements and compounds, their types and the differences between them in the article below.
What are Elements and Compounds ?
An element is a pure substance which consists of identical atoms or molecules with only one core of an atom.
A compound is a pure substance which consists of identical atoms or molecules with two or more different types of atomic core bound together.
What are Elements ?
In chemistry, an element is a pure substance that further cannot be broken down into a simpler form. Elements are the building blocks of all matter. They are identified by a distinct atomic number. The periodic chart organizes the elements by atomic number, highlighting elements with comparable properties. To date, 118 elements have been found, with many more in the process of discovery.
Classification of Elements
The elements are classified and grouped in the periodic table as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids based on their properties.
• Metals:- are elements that have a tendency to lose electrons in order to achieve stability, exhibiting electro positivity. Metals are further divided into three groups: Main Group Metals, Transition Metals, and f- block metals.
• Non-metals :- Non-metals are elements that have a tendency to gain electrons in order to achieve stability, i.e. they have electronegativity.
• Metalloids :- Metalloids are elements with characteristics that fall between metals and nonmetals.
Few Examples of Elements
Metals – Iron, Copper, Sodium, Aluminium, Lead
Non-Metals – Oxygen, Sulphur, Hydrogen, Argon, Chlorine
Metalloids – Silicon, Germanium, Boron, Arsenic
What are Compounds ?
Compounds are chemical substances composed of two or more elements chemically bonded together in a certain ratio. Chemically, compounds can be broken down into simpler types of matter (elements). When the elements join, some of their unique properties are lost, and the newly created compound has new properties.
Classification of Compounds
Compounds are classified as ionic compounds or covalent compounds based on their formation.
• Ionic compounds :- They are generated when a metal and a nonmetal combine. Because they include ions, they are also known as electrovalent compounds.
• Covalent compounds :- They are created when two non-metals interact. They are also referred to as molecular compounds.
Few Examples of Compounds
Water (H2O), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), sodium chloride (NaCl), carbon dioxide (CO2), calcium oxide (CaO), ammonia (NH3), methane (CH4), etc.
|
Parameters |
Elements |
Compounds |
|
Definition |
Elements are pure substances made up of only one type of atoms. |
Compounds are pure substances made up of two or more different types of elements. |
|
Composition |
Elements only have one type of atoms. The atomic number of each atoms is the same. |
Compounds are made up of different elements arranged in a certain order via chemical bonds. They only have one sort of molecules. |
|
Total Numbers |
There are a total of 118 elements. |
There are endless compounds. |
|
Classification |
Elements are classified as metals, |
Compounds are classified based on their bonds i.e. iconic |
|
|
non-metals and metalloids. |
compounds or covalent compounds. |
|
Representation |
Elements are represented by symbols and numbers. e.g. : Na, Cu, Fe, H, O |
Compounds are represented by chemical formulas. |
|
Ability to disassemble |
Chemical reactions cannot break down elements into simple ones. |
Chemical methods/reactions can spilt a compound into simpler components. |
|
Distinguished by |
Elements are identified by their atomic number. |
They are characterized by a constant ratio of different. |
What are Mixtures?
A mixture is an impure material composed of two or more separate chemical components that are not chemically bonded. A mixture’s constituents can be added in varying quantities. A mixture lacks a set chemical formula. It also lacks a definite melting and boiling point. It will exhibit the qualities of its constituents and can be deconstructed into them using simple methods.
Examples of mixtures are salt and water, sugar and salt, air, ethanol in water, etc.
Heterogeneous and Homogeneous Definition :
What is a Homogeneous Mixture?
These are the types of mixtures in which the components mixed are uniformly distributed throughout the mixture. In other words, “they are uniform throughout“. We can observe only one phase of matter in a homogeneous mixture. Key points regarding such mixtures are:
• Particles are distributed uniformly
• We can’t judge a homogeneous mixture by just seeing it
• Homogeneous mixtures are also called solutions
• Uniform composition
• Example: rainwater, vinegar, etc.
What is a Heterogeneous Mixture?
This is a type of mixture in which all the components are completely mixed and all the particles can be seen under a microscope. We can easily identify the components and more than one phase can be seen by naked eyes.
Key points regarding this type of mixtures :
• Particles are distributed non-uniformly
• We can judge a heterogeneous mixture by just seeing it’s nonuniform composition
Example : Seawater, pizza, etc.
Difference between Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Mixture
|
Homogeneous |
Heterogeneous |
|
It has a uniform composition. |
It has a non – uniform composition. |
|
It has only one phase |
There are two or more phases |
|
It can’t be separated out physically |
It can be separated out physically |
|
‘homo’ means the same |
‘hetero’ means different |
|
Example : a mixture of alcohol and water |
Example : a mixture of sodium chloride and sand |
Example :
Soft Drinks : Homogeneous or Heterogeneous mixture ?
In a homogenous mixture, all the components are uniformly distributed and in the soft drink, we find components are uniformly distributed and in the soft drink, we find components likes sweetener, carbon dioxide and water forming a single phase. Therefore, a soft drink is homogeneous mixture.