Curriculum
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
CONCEPT - 01 : General Introduction to Organic Chemistry
0/3ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 01
0/3CONCEPT - 02 : Structural Representation of Organic Compounds
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 02
0/3CONCEPT - 03 : Classification of Organic Compounds
0/2ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 03
0/2CONCEPT - 04 : Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 04
0/2CONCEPT - 05 : Homologous Series
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 05
0/2CONCEPT - 06 : Isomerism
0/3ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 06
0/2PRACTICE QUESTION SET
0/1
Text lesson
TOPIC – 02 : Catenation
Definition :
- Catenation can be defined as self-linking of atoms of an element to form chains and rings.
- This definition can be extended to include the formation of layers ( two dimensional catenation ) and space lattices ( three dimensional catenation ).
- It depends upon bond energy, size and bond length between the atoms of the same element.
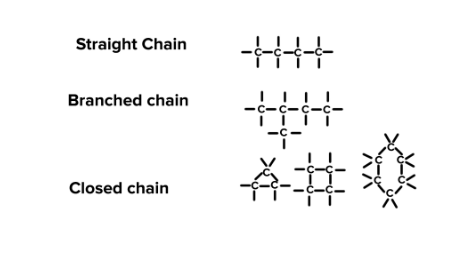
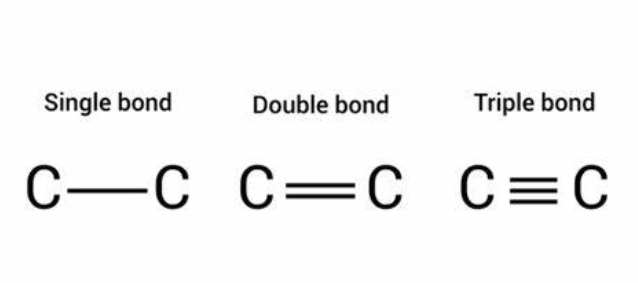
Subtopic : Why Carbon shows highest catenation property ?
- Carbon shows the property of catenation as it is small in size and has the ability to form stable covalent bonds with other carbon atoms to form a chain-like structure.
- The bond energy between the C-C bond is very high which enables them to form a long chain of C-C stable bonds.
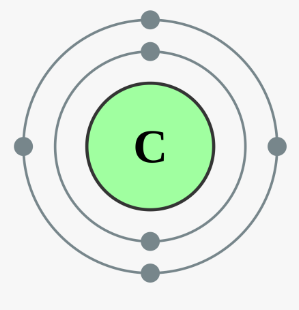
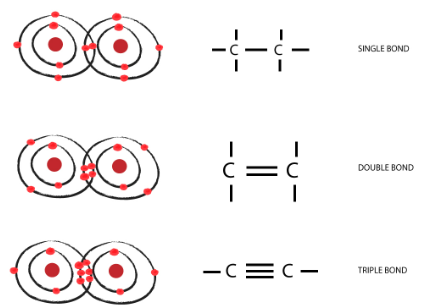
Figure : Electronic Configuration of
Carbon