Curriculum
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
CONCEPT - 01 : General Introduction to Organic Chemistry
0/3ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 01
0/3CONCEPT - 02 : Structural Representation of Organic Compounds
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 02
0/3CONCEPT - 03 : Classification of Organic Compounds
0/2ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 03
0/2CONCEPT - 04 : Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 04
0/2CONCEPT - 05 : Homologous Series
0/4ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 05
0/2CONCEPT - 06 : Isomerism
0/3ASSIGNMENTS : CONCEPT - 06
0/2PRACTICE QUESTION SET
0/1TOPIC – 02 : Homocyclic and Heterocyclic Compounds
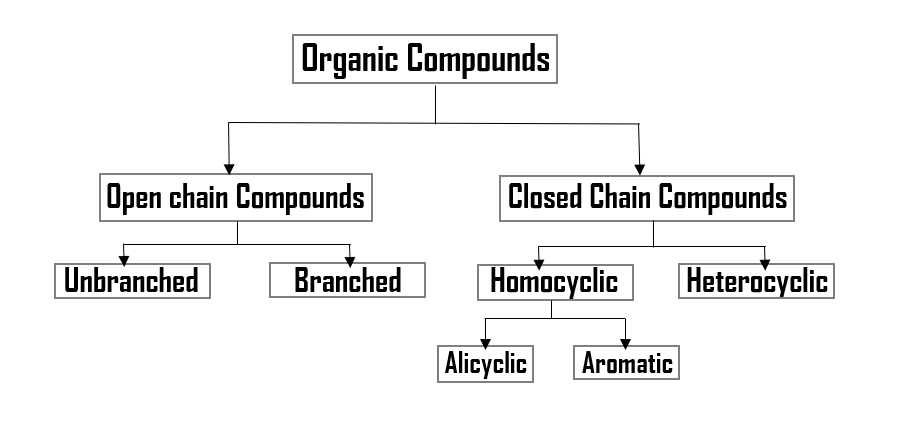
As we discussed earlier about the two kinds of organic compounds, namely, open chain compounds and closed chain compounds. Here, we are going to further classify the closed chain compounds. We have also different kinds of closed chain compounds that we are going to study under this topic.
1. Homocyclic Compounds : Homocyclic Compounds are ring structures made up of only carbon in the ring and hydrogen atoms. Without carbon & hydrogen there must not be presence of any other elements.
e.g.
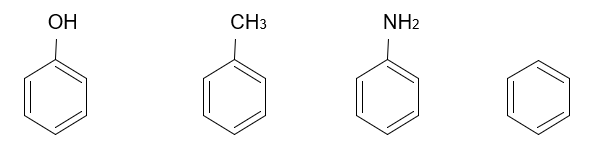
Phenol Toluene Aniline Benzene
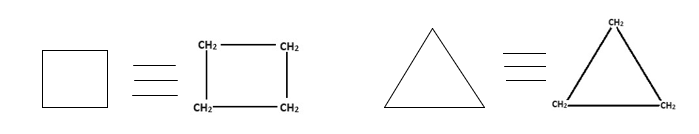
Cyclobutene Cyclopropane
Subtopic : Classification of Homocyclic compounds
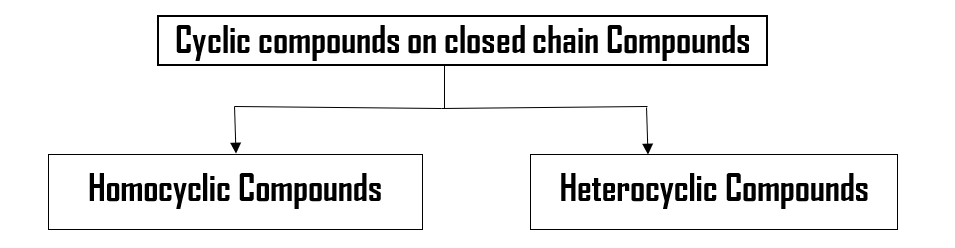
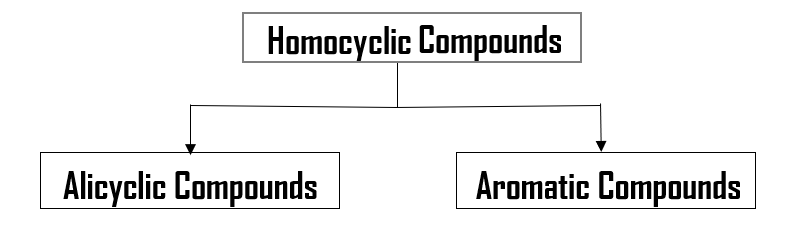
Now, this is worth mentioning that further classification of homocyclic compounds is also possible. Homocyclic compounds can be classified in two parts:
i. Alicyclic Compounds
ii. Aromatic Compounds
![]()
![]() SHAPE \* MERGEFORMAT
SHAPE \* MERGEFORMAT
|
Homocyclic |
|
|
|
Compounds |
|
|
i. Alicyclic Compounds : An alicyclic compound is defined as an organic compound, which is both cyclic and aliphatic .
e.g.

Cyclopropane Cyclobutane Cyclohexa-1,4-diene Cyclopentene
o-Phthaldialdehyde 2,3-Diaminonaphthalene
ii. Aromatic Compounds : Any planar system with full delocalisation of the pi-electron in the ring and (4n+2) pi electrons in the ring is said to be aromatic.
e.g.
![]()
![]()

Benzene Phenol Aniline Toluene
Naphthalene Furan
2. Heterocyclic Compounds : A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring.
e.g.
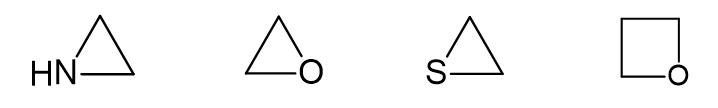
Aziridine Ethylene Oxide Thiirane Oxetane

Piperidine 1,4-dioxane